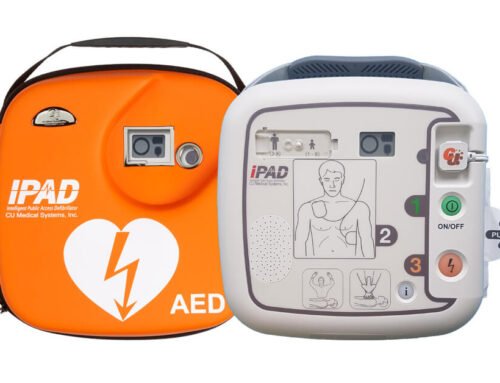
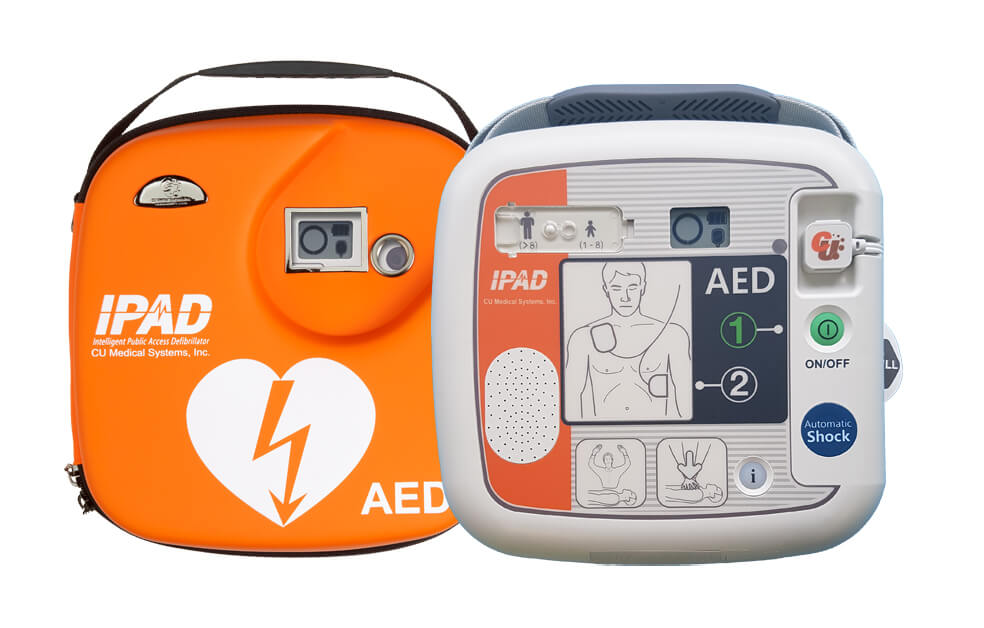
Understanding the Distinction: Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic Defibrillators
Understanding the Distinction: Semi-Automatic vs. Fully Automatic Defibrillators
Introduction:
In the realm of emergency medical equipment, defibrillators play a crucial role in saving lives during cardiac emergencies. Two common types of defibrillators are semi-automatic defibrillators (SAD) and fully automatic defibrillators (FAD). While both serve the same primary purpose – restoring a normal heart rhythm – there are key differences between the two. In this article, we’ll explore these distinctions to help you make an informed decision about which type of defibrillator is best suited for specific scenarios.
- Operation Mechanism:
- Semi-Automatic Defibrillators (SAD): SADs require the user to initiate the shock delivery by pressing a button after the device analyzes the patient’s heart rhythm. The user plays an active role in deciding when to administer the shock, ensuring they have assessed the situation and deemed it necessary.
- Fully Automatic Defibrillators (FAD): FADs, on the other hand, operate autonomously. Once the device analyzes the heart rhythm and determines that defibrillation is necessary, it delivers the shock automatically without requiring any manual input from the user.
- User Intervention:
- Semi-Automatic Defibrillators (SAD): SADs are designed to be user-friendly and often provide audible and visual prompts to guide the user through the resuscitation process. However, the decision to administer the shock ultimately rests with the user.
- Fully Automatic Defibrillators (FAD): FADs are designed for simplicity, eliminating the need for the user to press a button. This can be advantageous in situations where immediate action is crucial, as the device automatically delivers the shock when needed.
- Training and Certification:
- Semi-Automatic Defibrillators (SAD): Users of SADs typically undergo training to familiarize themselves with the device and gain the confidence to make critical decisions during an emergency. Basic life support (BLS) and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) training are often recommended.
- Fully Automatic Defibrillators (FAD): FADs are designed to be more straightforward, and users may require less training compared to SADs. However, CPR and AED training are still essential to ensure users can respond effectively in emergency situations.
Conclusion:
Choosing between a semi-automatic and fully automatic defibrillator depends on various factors, including the level of training of potential users and the specific use case. Both devices are instrumental in increasing the chances of survival during cardiac emergencies. Remember, quick access to and proper use of a defibrillator can make a significant difference in saving a life.
It’s important to note that for accurate visual representations of both types of defibrillators, you can refer to reputable medical equipment websites or manufacturers’ official pages. Some reliable sources include:
Always ensure that you’re consulting the latest information and guidelines for the most up-to-date insights into defibrillator technology.